- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
10-17-2017
08:30 PM
- edited on
02-06-2024
12:11 PM
by
Nils
![]()
This page explains how you can scan Windows computers with LsPush in a scheduled task.
Lansweeper includes several scanning methods to scan the assets in your network. You can scan the Linux, Unix, Mac and Windows computers, VMware servers and other devices in your network without installing any Lansweeper software on the machines you're scanning.
For Windows computers, however, you can choose to perform your scans with a scanning agent. Lansweeper's scanning agent is called LsPush. One of the ways it can be implemented is by using a scheduled task. LsPush is a small executable that scans the computer locally when run on a Windows computer. LsPush cannot and does not need to be installed on the computer you're scanning. The LsPush executable must simply be executed on the computer whenever you want to scan the machine. The LsPush scan results can be sent directly to your Lansweeper server for automatic processing or stored in a file that can be imported into your Lansweeper installation later on.
There are many ways to run LsPush on your machines. Any process that can run the LsPush executable, preferably with a parameter, can trigger LsPush scans of your machines. For instance, LsPush scans can be fully automated by integrating the scanning agent into logon scripts, group policies, or scheduled tasks.
This article explains how to scan Windows computers with the LsPush agent in a scheduled task and have the scan results automatically sent back to your Lansweeper server. This scanning approach could, for instance, be helpful if you have workgroup computers that you want to scan locally and in an automated way.
Scanning with LsPush in a scheduled task
To scan Windows computers with the LsPush scanning agent in a scheduled task, follow these steps:
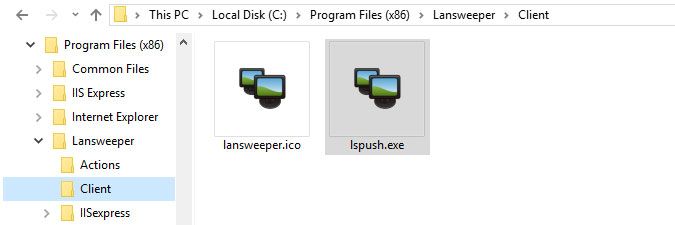
- On the machine hosting your Lansweeper installation, browse to
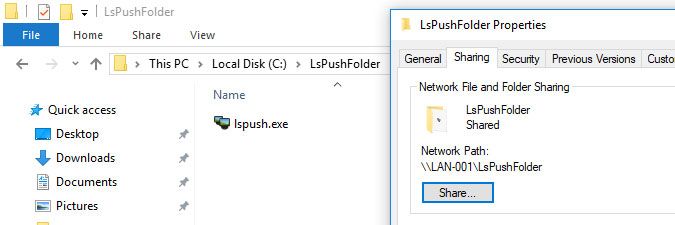
Program Files (x86)\Lansweeper\Clientand copy the LsPush executable contained within.When you update your Lansweeper installation, the latest version of the LsPush executable is automatically added to the Client folder on your Lansweeper server. Make sure to use the latest LsPush executable to scan your machines, as scanning with old agents can cause incomplete data to be returned. If you have just updated Lansweeper and are scanning with LsPush in a logon script, group policy or scheduled task, copy the up-to-date LsPush to any folder referenced by your script, policy or task. - Paste the LsPush executable into any shared folder that is accessible by the computers you want to scan.
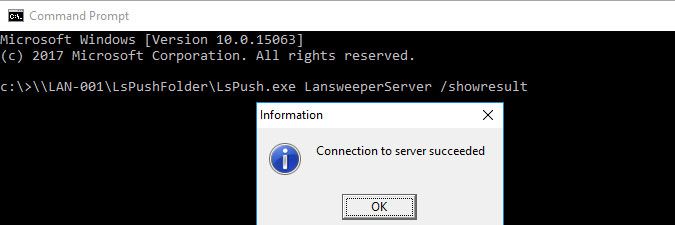
In the example below, we set up a shared folder on computer LAN-001. All scanned computers will be reading the LsPush executable from this folder.Do not share the Client folder on your Lansweeper server directly. Create your own shared folder and add a copy of the LsPush executable to this folder. Sharing the Client folder directly will result in access violations when updating Lansweeper. - For testing purposes, open Command Prompt on a computer you want to scan and run the command below, replacing
\\LAN-001\LsPushFolderwith the name of the shared folder storing your LsPush executable andLansweeperServerwith the name of your Lansweeper scanning server.
This command triggers a local scan of the computer and sends the scan results directly to your Lansweeper server for import. After a short while, you will receive visual feedback in a pop-up window indicating whether the connection to the Lansweeper server succeeded. This test is just to confirm the command works prior to implementing it in a scheduled task.
\\LAN-001\LsPushFolder\LsPush.exe LansweeperServer /showresult
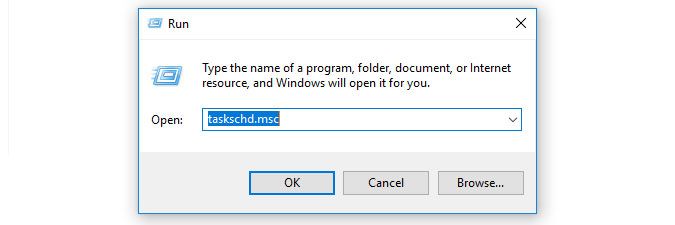
By default, LsPush traffic is sent to port 9524 on your Lansweeper server. If the test above does not succeed, make sure incoming traffic over port 9524 is allowed in your Lansweeper server's firewall settings. - On the computer you want to scan with LsPush in a scheduled task, open your Start menu and open Run.
-
In the input box, type "taskschd.msc" and click OK.
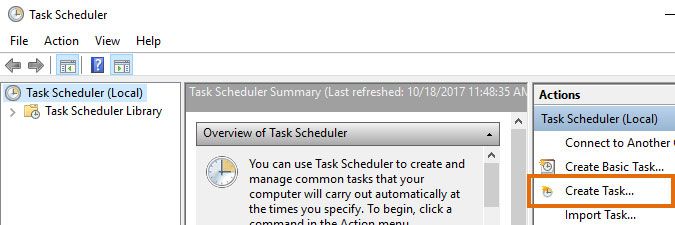
- Select Create Task... in the right pane.
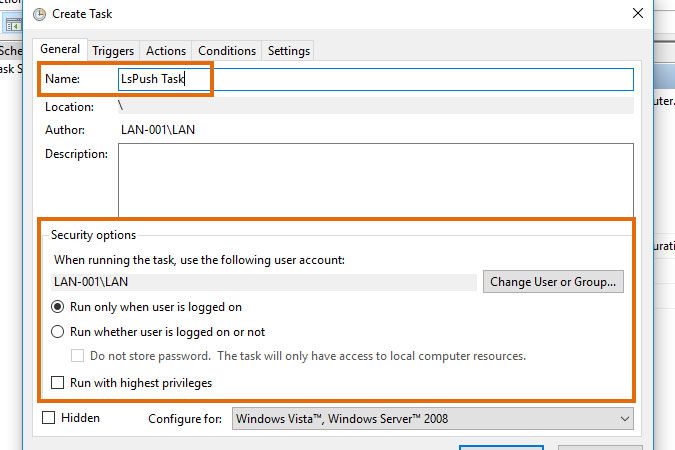
- In the General tab, give your task a name and specify which user account your task should run under. LsPush can scan almost all Windows computer data with a regular, non-admin user.
In the example below, we chose to run the task under user "LAN". -
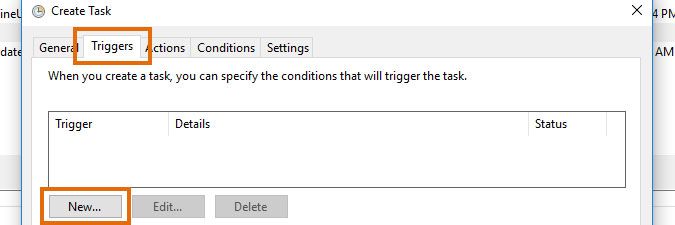
In the Triggers tab, click the New... button.
-
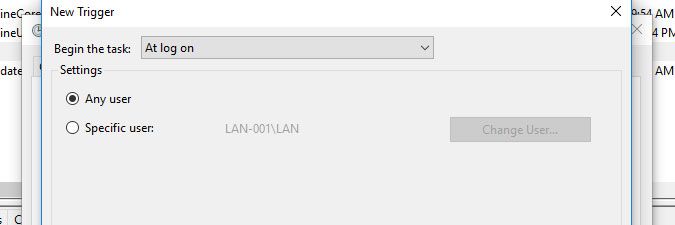
Specify the schedule you want to use to run the LsPush task and select OK.
In the example below, we chose to run the task at user logon, i.e. whenever a user logs into the computer. -
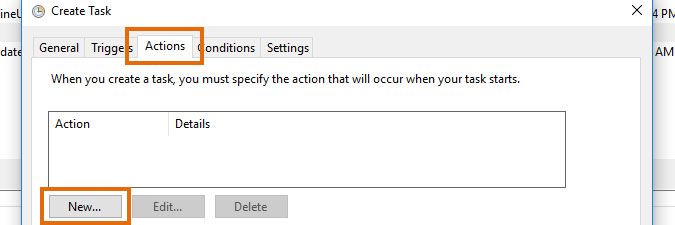
In the Actions tab, click the New... button.
-
Select Start a program from the dropdown menu.
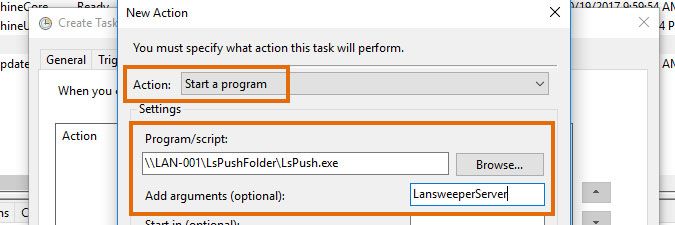
-
In the first input box, submit the file path of your LsPush executable.
-
In the second input box, submit the name of your Lansweeper scanning server and click OK.
-
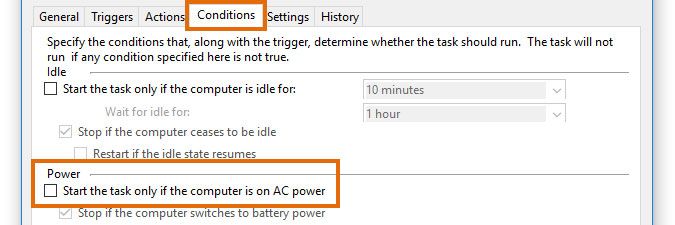
In the Conditions tab, uncheck Start the task only if the computer is on AC power. Unchecking this option is important for laptops, to ensure the task is executed even when running on battery power. Click OK afterward.
-
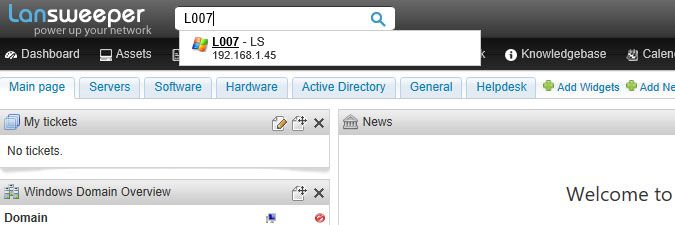
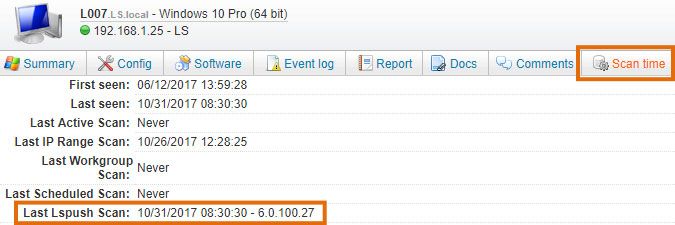
Once a user has logged into the computer to be scanned, perform a search for the name of the computer in the web console search bar, which takes you to the machine's Lansweeper webpage. The Scan time tab of the machine's asset page should also indicate an LsPush scan has taken place.
If the search bar finds no asset for the scanned computer, the LsPush scan may have failed for any of the following reasons: you've reached your Lansweeper license's asset limit, your Lansweeper database is full, the Windows computer is excluded from scanning.
Was this post helpful? Select Yes or No below!
Did you have a similar issue and a different solution? Or did you not find the information you needed? Create a post in our Community Forum for your fellow IT Heroes!
More questions? Browse our Quick Tech Solutions.